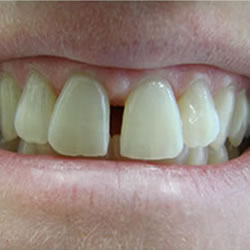
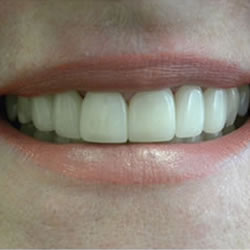
Are you embarrassed to smile because your teeth look yellow and dull? Many people are self conscious of their teeth due to discoloration that has occurred over the years. This had led to a boom in the dentistry area of teeth whitening. Americans spend over a billion dollars each year on over-the-counter whitening products, which doesn’t even count the people who seek whiter teeth through professional treatment.
It is likely that you have heard two terms related to brightening your smile: teeth bleaching and teeth whitening. Are these the same thing? Although their goals are similar, these terms refer to different processes for whitening your teeth.
Bleaching
The FDA requires that the word “bleaching” be used only in cases where the teeth are able to be whitened more than their natural color. This occurs only with products containing bleach, usually hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide.
Whitening
“Whitening” is the term used when the surface color of a tooth is restored by removing debris and dirt. For example, a cleaning product such as toothpaste is considered a whitening product instead of bleaching.
Which one is better?
Teeth whitening is a subjective procedure, meaning that it varies with each person. Before deciding how to brighten your smile, consult with your dentist to get a realistic idea of potential results for your teeth. That way you can choose the best process for you personally, and set your expectations about how long it might take and how your teeth may appear when complete. Whether you choose to bleach them or whiten them, it is likely that you will be dazzling your friends with your new, improved smile!
Teeth whitening dentist in Toronto
An estimated 69 percent of adults in this country have lost at least one tooth. While losing a tooth may not seem like a big deal, it can cause serious issues. Not only does your appearance suffer, but your oral health may also decline. Remaining teeth can shift causing additional wear on these teeth. Other teeth may also fall out, directly affecting your ability to eat.
If you have lost one or more teeth, talk with your dentist about choices to close the gaps in your smile. Replacement options include:
Dental Bridges
One of the most common choices, a dental bridge is a permanent replacement of a lost tooth. A dental bridge contains two dental crowns on each side and a false tooth in the middle. The two permanent teeth on either side of the gap serve as abutment teeth that hold the bridge in place. Once the bridge is cemented into your mouth, you cannot take it out.
Dentures
If you have lost all the teeth on the upper or lower arch, you will need a complete set of dentures. Dentures are rows of prosthetic teeth on a gum-colored base. Usually, dentures are held in position by either adhesive cream or suction. For more security, some patients opt for implant-supported dentures, which involve the surgical placement of four screws into the jaw bone. Your denture then snaps onto the posts, creating a secure fit.
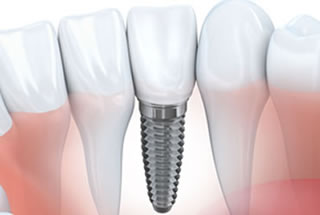
Dental Implants
The closest prosthetic to nature, a dental implant is a small metal post that the dental specialists at Metrowest Prosthodontics will place in your jawbone. One post is used for each missing teeth. Following implant surgery, your mouth will need time to heal, and the bone will fuse with the post, which forms the foundation for a permanent crown. Usually, the prosthetic replacement is placed three to six months after surgery. Implants look and function just like your natural teeth, giving you a full, attractive smile.
Your dental health is our priority at Yolanda Cruz DDS in Toronto Canada
For people with missing teeth, dentures can provide a new lease on life. Prosthetic replacements for lost teeth, dentures restore functionality, appearance, and confidence. After investing your time and money to get your custom dentures, make sure to keep them in good shape with proper care. Follow these tips to preserve the life cycle of your dentures:
• Clean your gums and tongue to promote good oral health
• Contact your dentist if you feel pain or discomfort after the adjustment period ends
• Floss the dentures as if they were your natural teeth, which removes food particles and prevents tartar build up
• If not wearing your false teeth, place them in a container with cold water
• Keep your dentures in a safe place away from young kids or pets
• Seat your dentures using thumb and finger pressure instead of biting down to put them in place
• Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean dentures every day.
• Watch what you eat because darker foods and beverages can stain your dentures.
• Wear your dentures as directed for the first few weeks; then, remove the prosthetic appliances when you sleep
Damage to Your Dentures
Sometimes, even with the best care, an accident will happen and your dentures will get broken. Call your dentist right away so that they can get you in as soon as possible. Don’t try to wear the appliance because you could cause more harm to the prosthetic as well as to your mouth.
Denture Dentist in Toronto – Dr. Cruz
Approximately 69 percent of adults in this country have lost at least one tooth. If not replaced, individuals with missing teeth risk losing up to 20 percent of adjacent teeth over the next four to eight years. Not only do missing teeth impact your dental health, but they can also make you look older and create limits in your diet. Dental implants provide modern, attractive replacements for missing teeth.
Fabricated from biocompatible titanium, a dental implant is a small, metal post surgically placed into your gum tissue. The implant acts as an artificial root for the prosthetic crown that anchors to the top of the post. One implant is used for each missing tooth. Dental implants are permanently positioned in your jaw, renewing the stability and strength of your smile. Your dentist can perform a complete evaluation to make sure you have sufficient bone structure to support the dental implants.
Usually, dental implant placement is a two-step process. During the first procedure, a specialist performs the surgery to position the implants into your jaw bone. Your mouth will need about three to six month for healing. During the healing, the bone will fuse to the implants, which forms a solid foundation for the porcelain crowns that your dentist will place on top of each implant during the 2nd procedure.
With dental implants, patients can once again smile confidently and eat the foods they love. Unlike dentures, implants won’t shift or require any adhesive creams. Treat your implants as you do your natural teeth with frequent brushing, regular flossing, and routine dental checkups. If well-cared for, dental implants have a 95 to 98 percent success rate.
Consider dental implants at the office of Dr. Yolanda Cruz
As early as 1550 BC, papyrus scrolls show that Hippocrates, the Greek physician viewed as the father of modern medicine, offered rinsing with a mouthwash of red wine, anise, and dill to produce sweet-smelling breath. An estimated 93 million Americans suffer from chronic bad breath, also called halitosis. Though bad breath won’t compromise your wellbeing, it can wreck your social life.
The following tactics can help you enjoy fresh breath:
Remember your tongue
Many people don’t realize that our tongues have millions of filaments that can trap food particles and bacteria, which may lead to bad breath. Along with brushing and flossing, make sure to clean your tongue with either a toothbrush or tongue scarper.
Keep sugarless gum handy
Saliva provides excellent defense against halitosis, and chewing sugarless gum encourages adequate saliva flow.
Try cinnamon
Though mint will help cover bad breath, a recent study suggests that cinnamon may reduce the bacteria that produce halitosis, so your breath will smell better.
Watch your diet
If you struggle with bad breath, avoid foods that can trigger mouth odor, such as coffee, alcohol, onions, and garlic. Certain diet plans, like Atkins, can create an unpleasant side effect from ketosis, the fat-burning state that occurs with this type of diet. Increasing your carb intake will help in this case.
Stay hydrated
Water helps wash away odor-causing bacteria. It also keeps your mouth moist, which prevents dry mouth, another issue that can lead to halitosis.
Are your teeth broken or cracked? Does your bite feel uncomfortable? Do you feel embarrassed about how your smile looks? If you answered yes to these questions, talk with your dentist about full-mouth rehabilitation.
Disease, trauma, and daily life can take a toll on your smile. Full-mouth rehabilitation is designed to revitalize your appearance, improve oral health, and restore harmony in your mouth. The full-mouth rehabilitation process usually combines cosmetic and restorative treatments to re-establish balance between your teeth, gums, bone tissue, and the related muscles.
As part of correcting your dental problems, your dentist will work with you to decide on a course of action that suits your goals, budget, and lifestyle. You will receive a thorough analysis of your whole mouth. Then, your dentist will make recommendations that may include the following procedures or some combination of these therapies:
• Porcelain veneers or cosmetic bonding to cover imperfections on existing teeth
• Dental implants or dentures to replace lost teeth
• Tooth-colored fillings or dental crowns to stabilize damaged teeth
• Root canal therapy to save a severely injured tooth and prevent extraction
• Periodontal therapy to stop gum disease and improve oral health
Typically, full-mouth rehabilitation involves a series of appointments. Once your dentist has created a detailed plan, you will visit the office over several visits so that the dental team can systematically repair your mouth and smile.

 E-Mail Us
E-Mail Us  416-595-5490
416-595-5490