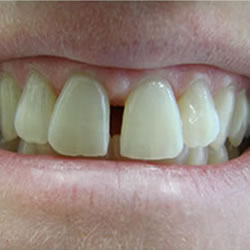
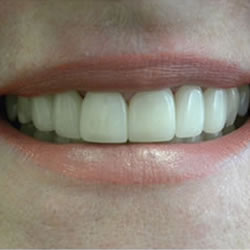
Healthy gums are vitally important to maintaining your teeth as you age. Taking vigilant care of your gums with proper oral hygiene, a healthy diet, and regular dental visits can help you to avoid gum disease and other gum related issues. Some medications and chronic illnesses can also make you more likely to develop gum disease, even if you practice excellent oral care.
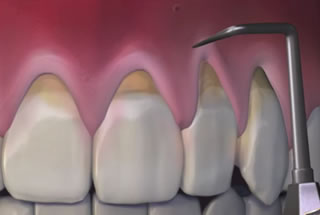
Dentists will first attempt to treat patients who have developed periodontal disease with non-surgical methods like scaling, root cleaning, and antibiotic treatment. If these treatments are unsuccessful, and you develop more severe complications, your dentist may recommend gum surgery to treat your gum disease or the resulting complications. Some of the most common surgical procedures to treat the problems that arise from gum disease include:
- Pocket reduction or flap surgery to clean, smooth and tighten the pockets around the base of the tooth.
- Bone grafts to replace bone lost from gum disease and create a base for bone growth.
- Soft tissue grafts to move tissue from the roof of the mouth to gums to add support to the teeth.
- Guided tissue regeneration to stimulate the growth of bone and soft tissues.
- Bone surgery to decrease the depth of holes created by advanced bone loss.
- Crown lengthening to remove overgrown gum tissue from the teeth and make them appear longer.
In most cases with regular exams and proper home oral care, you can prevent periodontal disease from developing to the point of surgery. However, if you find yourself needing surgical treatment for complications that are the result of gum disease, you should consult with a qualified oral surgeon immediately to avoid more severe damage to your oral health.

 E-Mail Us
E-Mail Us  416-595-5490
416-595-5490